Angle-of-Pull (AOP) Resistor Point Locator Prototype for Application in Physiotherapy
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/sijphpc.3.1.8196Keywords:
Physiotherapy, angle of pull, goniometerAbstract
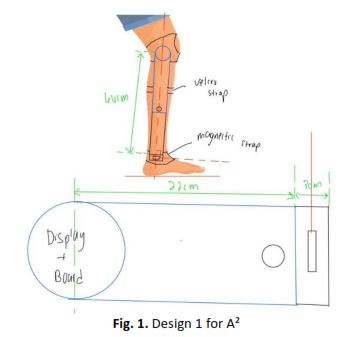
The increasing prevalence of musculoskeletal disorders necessitates the development of precise and user-friendly tools in physiotherapy to improve rehabilitation outcomes. Traditional methods for determining the Angle of Pull (AOP) and locating resistance points in clinical settings often lack accuracy and accessibility. To address this issue, this study introduces the Angle Assist (A²) device, aimed at enhancing the precision and effectiveness of rehabilitation exercises by accurately identifying the resistance point where the line of pull generates maximal muscle torque. The primary objective of this research was to design and develop a prototype for an AOP resistor point locator equipped with a precise angle reading display, aimed at reducing the time required to determine the AOP and pinpoint the resistance point by at least 10%. The methodology involved the integration of an MPU6050 sensor, an OLED display and laser pointers, all controlled by customized firmware. The device was subjected to a series of tests, including accuracy, reliability and time improvement test. The results demonstrate that the A² device achieves high accuracy, with an R² value of 0.9991 when compared to true angles. Additionally, the device exceeded the initial objective by reducing the time required to determine the AOP and pinpoint the resistance point by 16.92%. In conclusion, the A² device represents a significant advancement in physiotherapy practices by providing precise angle measurements and improving the accuracy of resistance point placement.