Radiation Dose Exposure from Routine CT Examination among Paediatric Patients: A Systematic Review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/sijphpc.3.1.3151Keywords:
Radiation dose, computed tomography, CT chest, CT abdomen-pelvis, paediatrics, image quality, radiation exposureAbstract
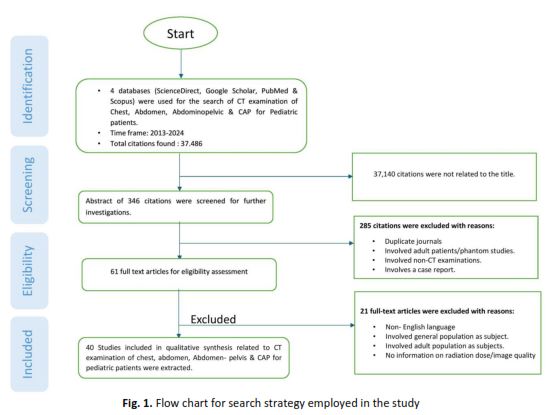
The increasing use of computed tomography (CT) in paediatric healthcare has raised concerns about radiation exposure and its potential carcinogenic effects. In this study, we carried out a systematic review to evaluate the radiation dose exposure from routine CT examinations in paediatric patients aged 0-20 years, covering studies published between 2013 and 2024. The review focuses on four types of CT examinations: CT Chest, CT Abdomen, CT Abdomen-Pelvis, and CT Chest-Abdomen-Pelvis (CAP). A comprehensive search across four databases, namely ScienceDirect, Google Scholar, PubMed, and Scopus, yielded 37,486 citations, from which 40 eligible studies were selected: 17 on CT Chest, 8 on CT Abdomen, 9 on CT Abdomen-Pelvis, and 6 on CT CAP. Key radiation dose indices, such as volume-weighted CT dose index (CTDIvol), effective dose (E), dose length product (DLP), and size-specific dose estimates (SSDE), were extracted and analysed. The highest mean values of CTDIvol, DLP, and E were observed in CT CAP for patients in the weight-based category >45 kg, with values of 7.80±2.80 mGy, 368.60±107 mGy·cm, and 10.79±3.97 mSv, respectively. The highest mean SSDE was found in CT Abdomen-Pelvis for patients weighing more than 45 kg, with a value of 11.80±4.61 mGy. Regarding image quality metrics, the highest image noise was observed in CT Abdomen for the 0-45 kg weight category, with a value of 21.0±4.5 HU. These findings underscore the importance of implementing body size or weight-based protocols, adjusting CT acquisition parameters, and utilizing advanced reconstruction techniques to achieve significant radiation dose reduction while maintaining diagnostic image quality. This review highlights the need for optimizing CT protocols to ensure radiation safety in paediatric imaging, with an emphasis on tailored strategies based on patient dimensions and cutting-edge technological interventions.